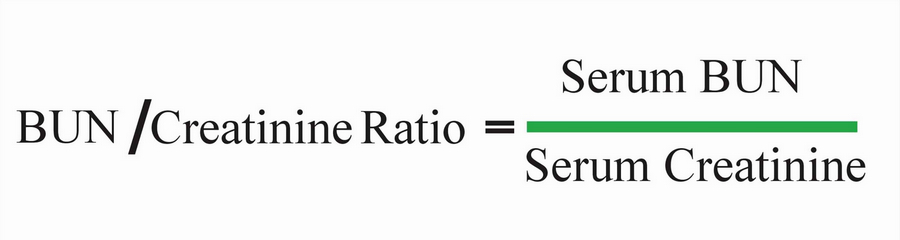What Causes a High BUN Creatinine Ratio
Final Word The BUN and creatinine are both end products of metabolism. The BUN and creatinine are waste products that need to be filtered by the kidneys and excreted through urination. A small amount of BUN and creatinine may be present in the blood and are just normal. However, if the ratios are too high or too low, it could signal that there is something wrong in your kidneys and liver. A high BUN and creatinine ratio could indicate a possible kidney-related problem.
BUN/Creatinine Ratio
The principle behind this ratio is the fact that both urea (BUN) and creatinine are freely filtered by the glomerulus; however, urea reabsorbed by the tubules can be regulated (increased or decreased) whereas creatinine reabsorption remains the same (minimal reabsorption).
The BUN/Creatinine ratio is useful in the differential diagnosis of acute or chronic renal disease. Reduced renal perfusion, e.g., congestive heart failure, or recent onset of urinary tract obstruction will result in an increase in BUN/Creatinine ratio. Increased urea formation also results in an increase in the ratio, e.g., gastrointestinal bleeding, trauma, etc. When there is decreased formation of urea as seen in liver disease, there is a decrease in the BUN/Creatinine ratio. In most cases of chronic renal disease the ratio remains relatively normal.
| Bun/Creatinine Ratio | 6-22 (calc) | ||||
| Urea Nitrogen (BUN) | |||||
| Age | Male (mg/dL) | Female (mg/dL) | |||
| 4-12 | 3-17 | ||||
| 1-11 Months | 2-13 | 4-14 | |||
| 1-3 Years | 3-12 | 3-14 | |||
| 4-19 Years | 7-20 | 7-20 | |||
| ≥20 Years | 7-25 | 7-25 | |||
| Creatinine | ||
| Age | Male (mg/dL) | Female (mg/dL) |
| ≤2 days | 0.79-1.58 | 0.79-1.58 |
| 3-27 days | 0.35-1.23 | 0.35-1.23 |
| 1 month-9 years | 0.20-0.73 | 0.20-0.73 |
| 10-12 years | 0.30-0.78 | 0.30-0.78 |
| 13-15 years | 0.40-1.05 | 0.40-1.00 |
| 16-17 years | 0.60-1.20 | 0.50-1.00 |
| 18-19 years | 0.60-1.26 | 0.50-1.00 |
| 20-49 years | 0.60-1.35 | 0.50-1.10 |
| 50-59 years | 0.70-1.33 | 0.50-1.05 |
| 60-69 years | 0.70-1.25 | 0.50-0.99 |
| 70-79 years | 0.70-1.18 | 0.60-0.93 |
| ≥80 years | 0.70-1.11 | 0.60-0.88 |
For patients >49 years of age, the upper reference limit for creatinine is approximately 13% higher for people identified as African-American.
What does it mean if your BUN/Creatinine Ratio result is too low?
A decreased ratio may be observed with liver disease and poor diet. Temporary levels that are high or low may not be a cause for concern and should be retested to confirm.
Understand and improve your laboratory results with our health dashboard.
Despite the arguments of political opponents to the contrary, premium increases had been going on for decades before the passage of the Affordable Care Act, also known as Obamacare. In fact, the average rate of yearly premium increases decreased after the law was passed in 2010, according to Forbes.
Upload your lab reports and get interpretation today.
Our technology helps to understand, combine, track, organize, and act on your medical lab test results.
What does it mean if your BUN/Creatinine Ratio result is too high?
An increased ratio of BUN to creatinine may be due to conditions that cause a decrease in the flow of blood to the kidneys, such as congestive heart failure or dehydration. It may also be seen with high protein blood levels or from gastrointestinal bleeding.
Interpret Your Lab Results
Upload your lab report and we’ll interpret and provide you with recomendations today.
What Causes a High BUN Creatinine Ratio?
The normal ratio of BUN to creatinine is between 10:1 and 20:1. A high BUN to creatinine ratio may be due to conditions that lead to decreased blood flow to the kidneys, such as congestive heart failure or dehydration.
BUN to creatinine ratios can increase with both age and muscle mass.
What is a BUN creatinine ratio?
Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine tests are blood tests that are performed as part of routine health screening. These tests help assess how well your kidneys are functioning. If your doctor suspects any kidney conditions, then the doctor will advise you to go for BUN tests.
BUN
BUN measures the amount of urea in your blood. Urea nitrogen is the waste product that is formed as your liver breaks down the proteins in foods you eat; this protein breakdown creates BUN.
Usually, BUN is removed by your kidneys. If your kidneys are not functioning properly, the BUN gets stored, resulting in increased BUN levels.
Creatinine
While BUN levels may vary, creatinine blood levels are mostly stable. Creatinine is a waste product that is formed as a result of muscle wear and tear. Creatinine is produced from creatine, a protein that helps produce energy for muscle contractions.
Creatinine is removed from the body by the kidneys. When there is an abnormal function of the kidneys, creatinine levels increase in the blood.
A BUN to creatinine ratio is used to check the health issues such as dehydration, kidney diseases, intestinal bleeding, and other conditions.
What causes abnormal BUN creatinine levels?
Abnormal BUN to creatinine levels are due to the underlying diseases and typically accompanied by the symptoms of the underlying conditions.
Causes of high BUN to creatinine levels include:
- Dehydration
- Intestinal bleeding
- Hyperthyroidism
- Congestive heart failure
- Kidney diseases
- Medications such as tetracycline and corticosteroids
Causes of low BUN to creatinine levels include:
- Malnutrition, with low protein intake
- Hyperthyroidism
- Advanced liver diseases (the liver cannot produce enough urea)
- Sickle cell anemia (kidneys absorb too little urea)
- Rhabdomyolysis (muscles break down rapidly)
- Kidney damage
- Medications such as acetazolamide and diuretics for conditions such as glaucoma, altitude sickness, and heart failure
What factors can increase or decrease BUN creatinine ratio?
Factors that increase BUN
- Increased dietary protein
- Alcohol consumption
Factors that reduce BUN
- Proper hydration
- Obesity and high BMI (which can cause kidney dysfunction)
Factors that reduce creatinine
- Not consuming creatinine and creatine-based food
- Increased dietary fiber
- Weight loss, which can improve kidney health
Factors that increase creatinine
- Increased exercise and physical activity
- Avoiding alcohol
SLIDESHOW
Health Solutions From Our Sponsors
- Penis Curved When Erect
- Could I have CAD?
- Treat Bent Fingers
- Treat HR+, HER2- MBC
- Tired of Dandruff?
- Life with Cancer
Medically Reviewed on 11/2/2022
References
Image Source: iStock image
Top What Causes a High BUN Creatinine Ratio Related Articles
Creatinine Blood Test
Creatinine is a chemical waste molecule that is generated from muscle metabolism. Creatinine is produced from creatine, a molecule of major importance for energy production in muscles. Creatinine has been found to be a fairly reliable indicator of kidney function. As the kidneys become impaired the creatinine level in the blood will rise. Normal levels of creatinine in the blood vary from gender and age of the individual.
How Can I Check My Kidneys at Home?
Albumin home test kits and smartphone-enabled home urinalysis devices are available to check your kidney function at home.
Kidney Health: Conditions That Affect Your Kidneys
Your kidneys help filter all the waste products your body builds up in its natural processes. Learn more from WebMD about the medical problems that can harm them.
Kidney Health: Warning Signs of Kidney Problems
Your kidneys are your body’s clearinghouse for toxins. Learn what swollen feet, muscle cramps, and other warning signs may signal about your kidneys’ health.
Kidneys Picture
The kidneys are a pair of organs located in the back of the abdomen. See a picture of the Kidneys and learn more about the health topic.
Surprising Things That Can Hurt Your Kidneys
Your kidneys do a lot for you. But are you helping or hurting them? Click through the WebMD quiz to find out how you might be damaging your kidneys without even knowing it.
Urea Breath Test
The urea breath test (UBT) is a test used to diagnose the presence of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) bacteria in the stomach. H. pylori causes, ulcers, inflammation, and atrophy of the stomach. The urea breath test is fairly simple, with few side effects, risks, or complications.
Ways to Keep Your Kidneys Healthy
You might know that more than a drink or two a day is bad for your health. But in some cases, any alcohol at all may not be a great idea.
What Are the Benefits of Creatine?
Creatine is a popular supplement in the fitness industry for improving lean muscle mass, building stamina and boosting exercise ability.
What Are the First Signs of Kidney Problems?
Keeping an eye out for these early warning signs of kidney problems can help you detect and treat the condition in a timely manner.
What Causes High Creatinine Levels?
A spontaneous elevation of creatinine may be caused by certain medications or dietary changes; however, persistently high creatinine levels could indicate kidney damage.
What Is the Purpose of Urea?
Urea is a nitrogenous waste product that is produced in the body. The liver breaks down protein and ammonia to make urea. Further, it is taken up by the kidneys. The kidneys filter the blood and transfer the urea from the blood to the urine. Thus, urea serves the purpose of expelling extra nitrogen and nitrogenous products from the body.
BUN/Creatinine Ratio Understand (High vs. Low Levels, Normal Range)
A BUN creatinine ratio is a blood work done to detect acute or chronic renal disease/failure.
Both BUN and creatinine are filtered in the kidneys and excreted through urination and they are a perfect parameter for identifying the overall functions of the kidneys. (1, 2)
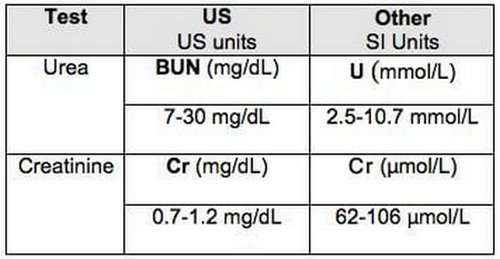
Image 1: The standard unit of measurements for BUN and creatinine.
Picture Source: lifeinthefastlane.com
Understanding the difference between BUN and creatinine test and their relationship
BUN Test
BUN stands for Blood Urea Nitrogen. The BUN test measures the level of nitrogen in the blood.
Doctors order this test to assess the functions of the kidneys and liver.
Nitrogen is urea’s waste product. The function of the kidneys is to filter the urea so that waste products will be removed from the body through urination.
The liver continuously produces urea and so it is just normal to have a small amount of urea in the blood. If the urea in the blood is abnormally high, it is an indicator that the kidneys are not functioning well.
There could be something wrong with your kidneys that need to be addressed properly and timely. (1, 2, 3)
Creatinine Test
A creatinine is a molecule produced by muscle metabolism. It is transported through the bloodstream and filtered in the kidneys and excreted through the urine.
The muscle mass of a person defines the rate of creatinine formation. Ideally, the level of creatinine remains constant throughout the day.
If the level of creatinine is high, then it indicates that there is something wrong with your kidneys. (3, 4)
Picture 2: BUN and creatinine ratio is measured using the above formula.
Photo Source: www.labpedia.net
What is a BUN creatinine ratio and its significance?
The BUN and creatinine test results are combined by the doctor to determine the BUN to creatinine ratio.
This is to find out the functions and overall condition of the liver and kidneys. It is used by the doctor in formulating an accurate diagnosis of health problems that have something to do with the kidneys.
Other reasons for taking BUN to creatinine ratio test include the following:
- Evaluate the functions of the kidneys
- Diagnose kidney-related diseases such as acute and/or chronic renal disease and urinary tract blockages
- Monitor the effectiveness of the treatments related to kidney problems
- It helps in diagnosing gastrointestinal bleeding
- It is useful in diagnosing severe dehydration (causes the BUN level to rise) (2, 3, 4, 5)
What can cause a high bun creatinine ratio?
- Congestive heart failure
- Urinary tract obstruction
- Gastrointestinal bleeding
- Trauma (5, 6)
What can cause a low BUN creatinine ratio?
- Liver-related diseases
- Low protein diet
- Severe polyuria and polydipsia
- Diabetes mellitus
- Cushing’s disease (6, 7)
What can cause an increase creatinine with normal BUN level?
- Severe muscle trauma
- Acute myositis
- Too much intake of ascorbic acid (vitamin C)
- Intake of cephalosporins (7)
What can cause a high BUN and normal creatinine?
- Gastrointestinal hemorrhage
- High protein diet
- Fever
- Intake of corticosteroids or tetracyclines (8, 9)
What can cause a low creatinine and normal BUN?
- Decrease muscle mass
- Severe cachexia (9, 10)
What to keep in mind before undergoing a BUN creatinine ratio test?
Your protein intake can significantly affect the test result. A high protein intake may cause an abnormally high level of BUN. On the other hand, a low protein intake may lead to an abnormally low level of BUN.
If you are going to undertake a BUN creatinine ratio test, make sure that you consume a normal amount of protein and that you are properly hydrated.
That way, you will be able to come up with an accurate BUN creatinine ratio test result. The result can also be affected by pregnancy. (2, 5, 8, 9)
“Click on image for the calculator”
Photo 3: A blood sample is drawn from the patient’s arm and sent immediately to the lab for testing and evaluation.
Image Source: lh3.googleusercontent.com
Image 4: BUN and creatinine are two parameters used to detect the condition of the kidneys.
Picture Source: i.ytimg.com
How is the test taken?
The procedure is performed by a lab technician. A blood is drawn from your upper arm using a sterile needle. The entire process would take around 5 to 10 minutes depending on the visibility of your vein.
What is a normal BUN and creatinine level ratio?
To get the BUN creatinine ratio, the BUN count is divided by the creatinine count.
What is the normal BUN creatinine ratio?
The ideal ratio is between 10:1 and 20:1. If the result is higher than the numbers mentioned, it indicates that there is a high level of BUN in the blood.
It is linked with kidney-related diseases or decreased flow of blood to the kidneys secondary to dehydration or congestive heart failure. If the result is below the normal ratio, then it could indicate malnutrition or liver-related diseases. (3, 6, 9, 10)
Final Word
The BUN and creatinine are both end products of metabolism. The BUN and creatinine are waste products that need to be filtered by the kidneys and excreted through urination.
A small amount of BUN and creatinine may be present in the blood and are just normal. However, if the ratios are too high or too low, it could signal that there is something wrong in your kidneys and liver.
A high BUN and creatinine ratio could indicate a possible kidney-related problem.
References:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BUN-to-creatinine_ratio
- https://www.questdiagnostics.com/testcenter/TestDetail.action?ntc=296
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/bun-to-creatinine-ratio
- https://www.healthlabs.com/bun-creatinine-ratio-testing
- https://acutecaretesting.org/en/articles/urea-and-creatinine-concentration-the-urea-creatinine-ratio
- https://lifeinthefastlane.com/ccc/ureacreatinine-ratio/
- https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/abs/10.1161/circheartfailure.112.968230
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/blood-urea-nitrogen/about/pac-20384821
- https://www.selfhacked.com/blog/bun-creatinine-ratio-high-low-levels-normal-range/
- https://www.beaumontlaboratory.com/test-lab-directory/lab-test-details/?testid=1305
Similar Posts:
- Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate ( eGFR) Test & Calculators
- Types of Blood Cells
- Urease Test
- Benedict’s Test
- Catalase Test