Label: NEOMYCIN AND POLYMYXIN B SULFATES AND HYDROCORTISONE OTIC SUSPENSION- neomycin and polymyxin b sulfates and hydrocortisone otic suspension
It is not active in vitro against Serratia marcescens and streptococci.
Neomycin and Polymyxin B Sulfates
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Nov 21, 2022.
On This Page
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Indications and Usage
- Contraindications
- Warnings
- Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Dosage and Administration
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
Neomycin and Polymyxin B Sulfates Description
Neomycin and Polymyxin B Sulfates Solution for Irrigation is a concentrated sterile antibiotic solution to be diluted for urinary bladder irrigation. Each mL contains neomycin sulfate equivalent to 40 mg neomycin base, 200,000 units polymyxin B sulfate, and water for injection.
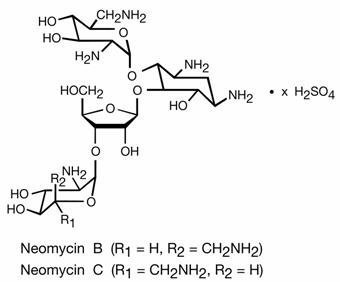
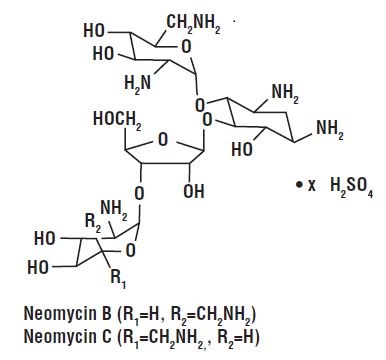
Neomycin sulfate, an antibiotic of the aminoglycoside group, is the sulfate salt of neomycin B and C produced by Streptomyces fradiae. It has a potency equivalent to not less than 600µg of neomycin per mg. The structural formulae are:
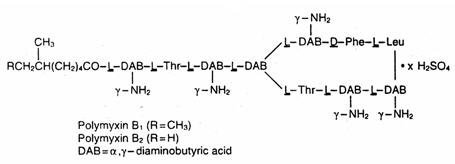
Polymyxin B sulfate, a polypeptide antibiotic, is the sulfate salt of polymyxin B 1 and B 2 produced by the growth of Bacillus polymyxa. It has a potency of not less than 6,000 polymyxin B units per mg. The structural formulae are:
Long wait times are often cited as a downfall of universal healthcare systems, but wait times in America have reached a new high, too. The average time to make a physician appointment as a new patient in 15 major U.S. cities is now 24 days, up 30% in just 3 years (2014 to 2018) according to physician recruiting firm Merritt Hawkins.
Neomycin and Polymyxin B Sulfates – Clinical Pharmacology
After prophylactic irrigation of the intact urinary bladder, neomycin and polymyxin B are absorbed in clinically insignificant quantities. A neomycin serum level of 0.1 µg/mL was observed in three of 33 patients receiving the rinse solution. This level is well below that which has been associated with neomycin-induced toxicity.
When used topically, polymyxin B sulfate and neomycin are rarely irritating.
Microbiology: The prepared Neomycin and Polymyxin B Sulfates Solution for Irrigation solution is bactericidal. The aminoglycosides act by inhibiting normal protein synthesis in susceptible microorganisms.
Polymyxins increase the permeability of bacterial cell wall membranes. The solution is active in vitro against
Escherichia coli
Staphylococcus aureus
Haemophilus influenzae
Klebsiella and Enterobacter sepecies
Neisseria species, and
Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
It is not active in vitro against Serratia marcescens and streptococci.
Bacterial resistance may develop following the use of the antibiotics in the catheter-rinse solution.
Indications and Usage for Neomycin and Polymyxin B Sulfates
Neomycin and Polymyxin B Sulfates Solution for Irrigation is indicated for short-term use (up to 10 days) as a continuous irrigant or rinse in the urinary bladder of abacteriuric patients to help prevent bacteriuria and gram-negative rod septicemia associated with the use of indwelling catheters.
Since organisms gain entrance to the bladder by way of, through, and around the catheter, significant bacteriuria is induced by bacterial multiplication in the bladder urine, in the mucoid film often present between catheter and urethra, and in other sites. Urinary tract infection may result from the repeated presence in the urine of large numbers of pathogenic bacteria. The use of closed systems with indwelling catheters has been shown to reduce the risk of infection. A three-way closed catheter system with constant neomycin-polymyxin B bladder rinse is indicated to prevent the development of infection while using indwelling catheters.
If uropathogens are isolated, they should be identified and tested for susceptibility so that appropriate antimicrobial therapy for systemic use can be initiated.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to neomycin, the polymyxins, or any ingredient in the solution is a contraindication to its use. A history of hypersensitivity or serious toxic reaction to an aminoglycoside may also contraindicate the use of any other aminoglycoside because of the known cross-sensitivity of patients to drugs of this class.
Warnings
PROPHYLACTIC BLADDER CARE WITH Neomycin and Polymyxin B Sulfates SOLUTION FOR IRRIGATION SHOULD NOT BE GIVEN WHERE THERE IS A POSSIBILITY OF SYSTEMIC ABSORPTION. Neomycin and Polymyxin B Sulfates SOLUTION FOR IRRIGATION SHOULD NOT BE USED FOR IRRIGATION OTHER THAN FOR THE URINARY BLADDER. Systemic absorption after topical application of neomycin to open wounds, burns, and granulating surfaces is significant and serum concentrations comparable to and often higher than those attained following oral and parenteral therapy have been reported. Absorption of neomycin from the denuded bladder surface has been reported. However, the likelihood of toxicity following topical irrigation of the intact urinary bladder with Neomycin and Polymyxin B Sulfates Solution for Irrigation is low since no appreciable amounts of these antibiotics enter the systemic circulation by this route if irrigation does not exceed 10 days.
Neomycin and Polymyxin B Sulfates Solution for Irrigation is intended for continuous prophylactic irrigation of the lumen of the intact urinary bladder of patients with indwelling catheters. Patients should be under constant supervision by a physician. Irrigation should be avoided in patients with defects in the bladder mucosa or bladder wall, such as vesical rupture, or in association with operative procedures on the bladder wall, because of the risk of toxicity due to systemic absorption following diffusion into absorptive tissues and spaces. When absorbed, neomycin and polymyxin B are nephrotoxic antibiotics, and the nephrotoxic potentials are additive. In addition, both antibiotics, when absorbed, are neurotoxins: neomycin can destroy fibers of the acoustic nerve causing permanent bilateral deafness; neomycin and polymyxin B are additive in their neuromuscular blocking effects, not only in terms of potency and duration, but also in terms of characteristics of the blocks produced.
Aminoglycosides, when absorbed, can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Aminoglycoside antibiotics cross the placenta and there have been several reports of total, irreversible, bilateral, congenital deafness in children whose mothers received streptomycin during pregnancy. Although serious side effects have not been reported in the treatment of pregnant women with other aminoglycosides, the potential for harm exists. If Neomycin and Polymyxin B Sulfates Solution for Irrigation is used during pregnancy, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus (See PRECAUTIONS ).
Precautions
General
Ototoxicity, nephrotoxicity, and neuromuscular blockade may occur if Neomycin and Polymyxin B Sulfates Solution for Irrigation ingredients are systemically absorbed (See WARNINGS ). Absorption of neomycin from the denuded bladder surface has been reported. Patients with impaired renal function, infants, dehydrated patients, elderly patients, and patients receiving high doses of prolonged treatment are especially at risk for the development of toxicity.
Irrigation of the bladder with Neomycin and Polymyxin B Sulfates Solution for Irrigation may result in overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms, including fungi. Appropriate measures should be taken if this occurs. The safety and effectiveness of the preparation for use in the care of patients with recent lower urinary tract surgery have not been established.
Urine specimens should be collected during prophylactic bladder care for urinalysis, culture, and susceptibility testing. Positive cultures suggest the presence of organisms which are resistant to the bladder rinse antibiotics.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category D. See WARNINGS section.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Adverse Reactions
Neomycin occasionally causes skin sensitization when applied topically; however, topical application to mucus membranes rarely results in local or systemic hypersensitivity reactions.
Irritation of the urinary bladder mucosa has been reported.
Signs of ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity have been reported following parenteral use of these drugs and following the oral and topical use of neomycin (See WARNINGS ).
Neomycin and Polymyxin B Sulfates Dosage and Administration
This preparation is specifically designed for use with “three-way” catheters or with other catheter systems permitting continuous irrigation of the urinary bladder. The usual irrigation dose is one 1-mL ampule a day for up to 10 days.
Using strict aseptic techniques, the contents of one 1-mL ampule of Neomycin and Polymyxin B Sulfates Solution for Irrigation should be added to a 1,000-mL container of isotonic saline solution. This container should then be connected to the inflow lumen of the “three-way” catheter which has been inserted with full aseptic precautions; use of a sterile lubricant is recommended during insertion of the catheter. The outflow lumen should be connected, via a sterile disposable plastic tube, to a disposable plastic collection bag. Stringent procedures, such as taping the inflow and outflow junction at the catheter, should be observed when necessary to insure the junctional integrity of the system.
For most patients, the inflow rate of the 1,000-mL saline solution of neomycin and polymyxin B should be adjusted to a slow drip to deliver about 1,000 mL every 24 hours. If the patient’s urine output exceeds 2 liters per day, it is recommended that the inflow rate be adjusted to deliver 2,000 mL of the solution in a 24 hour period.
It is important that the rinse of the bladder be continuous; the inflow or rinse solution should not be interrupted for more than a few minutes.
Preparation of the irrigation solution should be performed with strict aseptic techniques. The prepared solution should be stored at 4° C, and should be used within 48 hours following preparation to reduce the risk of contamination with resistant microorganisms.
How is Neomycin and Polymyxin B Sulfates Supplied
Sterile Neomycin and Polymyxin B Sulfate Solution for Irrigation is available in 1 mL ampules, cartons of 10 and 50.
Refrigerate at 2°-8° C (36°-46° F).
Literature Revised: August 2010
Product No.: 0801-81
Manufactured by:
Hikma Farmaceutica (Portuagal)
S.A. 2705-906 Terrugem SNT,
Portugal
Distributed by:
Watson Pharma, Inc.
Corona, CA 92880 USA PIN228-WAT/1
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
0591-2190-45
Sterile 10 x 1 mL Ampules
Neomycin and
Polymyxin B
Sulfates Solution
for Irrigation USP
NOT FOR INJECTION
Rx Only
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
0591-2190-50
Sterile 50x 1 mL Ampules
Neomycin and Polymyxin B
Sulfates Solution
for Irrigation USP
NOT FOR INJECTION
Rx Only
| Product Information | |||
| Product Type | HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL | Item Code (Source) | NDC:0591-2190 |
| Route of Administration | IRRIGATION | DEA Schedule | |
| Active Ingredient/Active Moiety | ||
| Ingredient Name | Basis of Strength | Strength |
| NEOMYCIN SULFATE (NEOMYCIN) | NEOMYCIN | 40 mg in 1 mL |
| POLYMYXIN B SULFATE (POLYMYXIN B) | POLYMYXIN B | 200000 [USP’U] in 1 mL |
| Inactive Ingredients | |
| Ingredient Name | Strength |
| WATER | |
| Packaging | |||
| # | Item Code | Package Description | |
| 1 | NDC:0591-2190-45 | 10 AMPULE in 1 CARTON | |
| 1 | NDC:0591-2190-54 | 1 mL in 1 AMPULE | |
| 2 | NDC:0591-2190-50 | 50 AMPULE in 1 CARTON | |
| 2 | NDC:0591-2190-54 | 1 mL in 1 AMPULE | |
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| ANDA | ANDA062664 | 10/25/2010 | 07/31/2020 |
| Labeler – Actavis Pharma, Inc. (119723554) |
Actavis Pharma, Inc.
More about neomycin / polymyxin b topical
- Check interactions
- Pricing & coupons
- Side effects
- Drug class: topical antibiotics
Patient resources
- Advanced Reading
- Neomycin and Polymyxin B
Label: NEOMYCIN AND POLYMYXIN B SULFATES AND HYDROCORTISONE OTIC SUSPENSION- neomycin and polymyxin b sulfates and hydrocortisone otic suspension
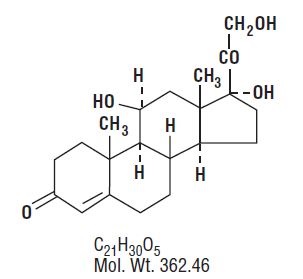
Neomycin and Polymyxin B Sulfates and Hydrocortisone Otic Suspension, USP is a sterile antibacterial and anti-inflammatory suspension for otic use. Each mL contains: neomycin sulfate equivalent to 3.5 mg neomycin base, polymyxin B sulfate equivalent to 10,000 polymyxin B units, and hydrocortisone 10 mg (1%). The vehicle contains thimerosal 0.01% (added as a preservative) and the inactive ingredients cetyl alcohol, propylene glycol, polysorbate 80, and Water for Injection. Sulfuric acid may be added to adjust pH. Neomycin sulfate is the sulfate salt of neomycin B and C, which are produced by the growth of Streptomyces fradiae Waksman (Fam. Streptomycetaceae). It has a potency equivalent of not less than 600 mcg of neomycin standard per mg, calculated on an anhydrous basis. The structural formulae are:
Polymyxin B sulfate is the sulfate salt of polymyxin B1 and B2, which are produced by the growth of Bacillus polymyxa (Prazmowski) Migula (Fam. Bacillaceae). It has a potency of not less than 6,000 polymyxin B units per mg, calculated on an anhydrous basis. The structural formulae are: 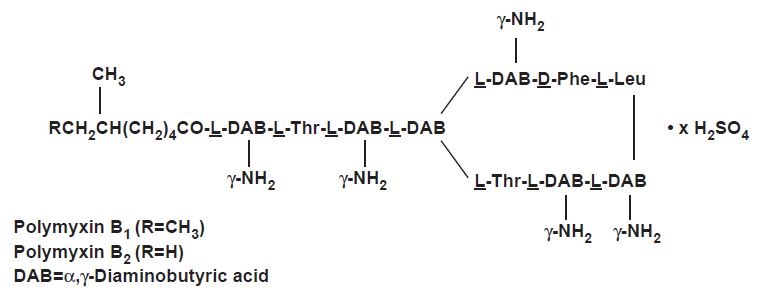
Corticoids suppress the inflammatory response to a variety of agents and they may delay healing. Since corticoids may inhibit the body’s defense mechanism against infection, a concomitant antimicrobial drug may be used when this inhibition is considered to be clinically significant in a particular case. The anti-infective components in the combination are included to provide action against specific organisms susceptible to them. Neomycin sulfate and polymyxin B sulfate together are considered active against the following microorganisms: Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Haemophilus influenzae, Klebsiella-Enterobacter species, Neisseria species and Pseudomonas aeruginosa . This product does not provide adequate coverage against Serratia marcescens and streptococci, including Streptococcus pneumoniae . The relative potency of corticosteroids depends on the molecular structure, concentration, and release from the vehicle.
For the treatment of superficial bacterial infections of the external auditory canal caused by organisms susceptible to the action of the antibiotics, and for the treatment of infections of mastoidectomy and fenestration cavities caused by organisms susceptible to the antibiotics.
This product is contraindicated in those individuals who have shown hypersensitivity to any of its components, and in herpes simplex, vaccinia, and varicella infections.
Neomycin can induce permanent sensorineural hearing loss due to cochlear damage, mainly destruction of hair cells in the organ of Corti. The risk is greater with prolonged use. Therapy should be limited to 10 consecutive days (see PRECAUTIONS-General ). Patients being treated with eardrops containing neomycin should be under close clinical observation. Neomycin and Polymyxin B Sulfates and Hydrocortisone Otic Suspension should not be used in any patient with a perforated tympanic membrane. Discontinue promptly if sensitization or irritation occurs. Neomycin sulfate may cause cutaneous sensitization. A precise incidence of hypersensitivity reactions (primarily skin rash) due to topical neomycin is not known. When using neomycin-containing products to control secondary infection in the chronic dermatoses, such as chronic otitis externa or stasis dermatitis, it should be borne in mind that the skin in these conditions is more liable than is normal skin to become sensitized to many substances, including neomycin. The manifestation of sensitization to neomycin is usually a low-grade reddening with swelling, dry scaling, and itching; it may be manifest simply as a failure to heal. Periodic examination for such signs is advisable, and the patient should be told to discontinue the product if they are observed. These symptoms regress quickly on withdrawing the medication. Neomycin containing applications should be avoided for the patient thereafter.
General:
As with other antibiotic preparations, prolonged use may result in overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms, including fungi. If the infection is not improved after 1 week, cultures and susceptibility tests should be repeated to verify the identity of the organism and to determine whether therapy should be changed. Treatment should not be continued for longer than 10 days. Allergic cross-reactions may occur which could prevent the use of any or all of the following antibiotics for the treatment of future infections: kanamycin, paromomycin, streptomycin, and possibly gentamicin.
Information for Patients:
Avoid contaminating the bottle tip with material from the ear, fingers, or other source. This caution is necessary if the sterility of the drops is to be preserved. If sensitization or irritation occurs, discontinue use immediately and contact your physician. SHAKE WELL BEFORE USING.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility:
Long-term studies in animals (rats, rabbits, mice) showed no evidence of carcinogenicity attributable to oral administration of corticosteroids.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects:
Corticosteroids have been shown to be teratogenic in rabbits when applied topically at concentrations of 0.5% on days 6 to 18 of gestation and in mice when applied topically at a concentration of 15% on days 10 to 13 of gestation. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Corticosteroids should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nursing Mothers:
Hydrocortisone appears in human milk following oral administration of the drug. Since systemic absorption of hydrocortisone may occur when applied topically, caution should be exercised when neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates and hydrocortisone otic suspension is used by a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use:
The safety and effectiveness of neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates and hydrocortisone otic suspension in otitis externa have been established in pediatric patients.
Geriatric Use:
Clinical studies of neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates and hydrocortisone otic suspension did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients.
Neomycin occasionally causes skin sensitization. Ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity have also been reported (see WARNINGS ). Adverse reactions have occurred with topical use of antibiotic combinations including neomycin and polymyxin B. Exact incidence figures are not available since no denominator of treated patients is available. The reaction occurring most often is allergic sensitization. The following local adverse reactions have been reported with topical corticosteroids, especially under occlusive dressings: burning, itching, irritation, dryness, folliculitis, hypertrichosis, acneiform eruptions, hypopigmentation, perioral dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, maceration of the skin, secondary infection, skin atrophy, striae and miliaria. Stinging and burning have been reported rarely when this drug has gained access to the middle ear. To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Rising Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-866-562-4597 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Therapy with this product should be limited to 10 consecutive days. The external auditory canal should be thoroughly cleansed and dried with a sterile cotton applicator. For adults, 4 drops of the suspension should be instilled into the affected ear 3 or 4 times daily. For children, 3 drops are suggested because of the smaller capacity of the ear canal. The patient should lie with the affected ear upward and then the drops should be instilled. This position should be maintained for 5 minutes to facilitate penetration of the drops into the ear canal. Repeat, if necessary, for the opposite ear. If preferred, a cotton wick may be inserted into the canal and then the cotton may be saturated with the suspension. This wick should be kept moist by adding further suspension every 4 hours. The wick should be replaced at least once every 24 hours. SHAKE WELL BEFORE USING.
10 mL bottle (NDC 68788-7787-1). Store at 15° to 25°C (59° to 77°F). Rx only
KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN.
Distributed by:
Rising Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Saddle Brook, NJ 07663
Code No.: TS/DRUGS/13/2010
Issued: 04/2019
Relabeled By: Preferred Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Neomycin and Polymyxin B Sulfates and Hydrocortisone Otic Suspension, USP
Sterile