Headache Behind Left Eye: 13 Causes with Treatments
Other signs and symptoms of eyestrain include:
Headache Behind the Eye? Why It Happens, What Helps
If you feel pain behind your eyes, there are many possible causes. There’s a good chance it could be a specific type of headache.
Causes of Headache Behind the Eye
Migraine headaches
These headaches often begin with pain around your eye and temple. They can spread to the back of your head. You might also have an aura , which can include visual signs like a halo or flashing lights that sometimes come before the pain starts.
You may also have nausea, a runny nose, or congestion. You could be sensitive to light, sounds, or smells. Migraine headaches can last several hours to a few days.
Tension headaches
Nearly 60% of Americans surveyed support a Medicare for All program, according to Business Insider. Those in favor of Medicare for All include 75% of Democrats, 58% of registered Independents and 36% of Republicans, though Republican support jumps up to 64% when discussing an optional expanded Medicare program, also referred to as “Medicare for Some.”
These are the most common type of headache. They usually cause a dull pain on both sides of your head or across the front of your head, behind your eyes. Your shoulders and neck may also hurt. Tension headaches might last 20 minutes to a few hours.
Cluster headaches
These cause severe pain around your eyes, often around just one eye. They usually come in groups. You may have several of them every day for weeks and then not have any for a year or more before they start again.
Along with the pain, you may also have watery eyes, congestion, and a red, flushed face. The attacks last 30 to 60 minutes and are so strong that you may be restless and can’t stand still while they happen. Cluster headaches aren’t very common and mostly happen in men.
Sinus headaches
A sinus infection (sinusitis) can cause a headache around your eyes, nose, forehead, cheeks, and upper teeth. This is where your sinuses are. You’ll often also have a fever, congestion, and a thick nasal discharge. The pain usually gets worse throughout the day.
True sinus headaches are rare. Migraine and cluster headaches are often mistaken for sinus headaches.
Eyestrain
This is when your eyes get tired from working too hard from doing things like staring at a computer screen or driving for a long time.
Other symptoms can include:
- Sore, itching, burning eyes
- Watery eyes
- Blurred vision
- Sore shoulders or back
Eyestrain isn’t serious and usually goes away when you rest your eyes.
Headache Behind the Eye Triggers
Different things may set off each type of headache.
You might get migraines because of:
- A lack of sleep
- Weather changes
- Stress
- Lights
- Noises
- Smells
- Things you eat or drink, like alcohol, chocolate, or MSG
- Missing a meal
Things that may give you a tension headache include:
- Stress
- Eyestrain
- Poor posture
- Problems with the muscles or joints in your neck or jaw
- Fatigue
- Dehydration or missing a meal
- Bright sunlight
- Noise
- Certain smells
Cluster headaches are often triggered by alcohol, smoking, or certain medications.
Headache Behind the Eye Treatment
Learning to avoid your triggers may prevent headaches or make them less painful. If you do get one, there are many kinds of treatments.
Medication for headache behind the eye
Over-the-counter pain medicine can ease occasional headaches. It may even help with migraine if you take it early enough. Doctors often recommend acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs ( NSAIDs ) like ibuprofen or naproxen. But remember that taking them too often can trigger overuse headaches.
If you get frequent tension headaches, your doctor may prescribe medication. Antidepressants like amitriptyline help many people.
Sometimes, prescription drugs are the only things that will ease migraine pain. Some of the most common are triptans such as almotriptan (Axert), eletriptan (Relpax), rizatriptan (Maxalt), sumatriptan (Imitrex), and zolmitriptan (Zomig). They help most people within 2 hours if taken early enough. People who get chronic migraines often take medicine like beta-blockers or antidepressants every day to help cut back on how many they have.
Breathing pure oxygen may bring relief of cluster headaches. Injected triptans like sumatriptan and lidocaine nose drops might also help. Some people take medicines such as verapamil (Calan, Verelan) or prednisone to prevent attacks.
Treat a sinus headache by clearing up the infection. Your doctor might suggest antibiotics and decongestants.
Home remedies for headache behind the eye
Caffeine or ice packs may help with migraine pain.
For a tension headache, try a heating pad or a warm shower, or rest until the headache goes away. It can also help to find better ways to handle stress. Learn relaxation techniques like yoga or deep breathing. Try not to skip meals or get too tired.
When you have a sinus infection, breathe in warm, moist air from a vaporizer or a pot of boiling water to ease congestion. Warm compresses can also help.
If your eyes are often strained, take breaks and blink more. Artificial tears may also refresh your eyes. Check with your doctor to make sure your vision prescription is up to date, and ask about exercises to strengthen eye muscles.
Waking Up With a Headache Behind the Eyes?
If you wake up in the morning with a pounding headache behind your eyes, you’re not alone. Here’s a look at some common causes of morning headaches:
Hangovers. After drinking too much alcohol, when your blood alcohol content drops back to normal or close to it, you start to feel symptoms that can include headaches. They can be caused by a couple of things. When you drink, the alcohol causes your body to make more urine, which can cause you to become dehydrated . The alcohol also causes your blood vessels to expand, which can lead to headaches. If you have more severe symptoms like confusion, seizures, slow breathing, or loss of consciousness, get medical help right away.
Migraine. The most common time for a migraine to happen is the early morning as pain medication you took before you went to sleep begins to wear off. But migraine headaches are complicated. They’re different for everybody. If you have a migraine or headache of any type that continually wakes you in the morning and gets in the way of your work or personal life, a doctor’s visit may be in order. Treatments, including over-the-counter and prescription medications, are available.
Sleep apnea. This is a condition where your throat muscles partially collapse while you sleep and interrupt your breathing. Other signs of sleep apnea include dry mouth and snoring. Sleep apnea is a serious health problem. Your doctor may suggest that you do a sleep test. A continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine might help, and lifestyle changes like losing weight and rolling off your back while you sleep could also help you get better rest.
Other sleep disorders. The relationship between sleep and headaches is a tricky one. Sometimes headaches are the cause of poor sleep, sometimes they’re the result of it. If it’s hard to get to sleep, stay asleep, or if you just wake up too early, you may have insomnia. It’s been tied to some forms of chronic headaches, including morning headaches. Circadian rhythm sleep disorders mess with when you fall to sleep or wake up. They can lead to morning headaches, too. If you think you may have a sleep disorder, see your doctor.
Overmedication. A medication overuse headache (MOH) can happen if you’re already prone to headaches and you take a lot of pain meds. A MOH usually hits right when you wake up. For those with chronic headaches, using medication more than 2 or 3 days a week may be too much. Check with your doctor about this. They can help you treat your headaches without overusing pain meds.
TMJ. The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) connects your jaw to your skull. Pain in the joint and its surrounding muscles, caused by things like too much gum chewing or clenching and grinding your teeth at night, can bring a morning headache. A dentist can prescribe an oral device to keep you from grinding your teeth at night.
Show Sources
digitalskillet / Getty Images.
Harvard Health Publishing: “Headache: When to worry, what to do.”
Cleveland Clinic: “Headaches in Adults.”
National Headache Foundation: “The Complete Headache Chart.”
Mayo Clinic: “Eyestrain.”
National Health Service (U.K.): “Tension-type headaches.”
Mayo Clinic: “Cluster headache.”
UpToDate: “Acute treatment of migraine in adults,” “Preventive treatment of migraine in adults.”
Cleveland Clinic: “Sinus Headaches,” “Headaches.”
University of Michigan Kellogg Eye Center: “Eye Strain.”
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke: “Migraine Information Page.”
The Migraine Trust: “More than “just” a headache.”
American Migraine Foundation: “Sleep Disorders and Headache.”
National Headache Foundation: “Headache Categories,” “Early Morning Awakening Headache.”
Mayo Clinic: “Headaches: Treatment depends on your diagnosis and symptoms,” “Hangovers.” “Insomnia.”
Rains, J. Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports , March 2008.
Paiva, T. Headache , Nov.-Dec.1995.
American Lung Association: “Learn About Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA),” “Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) Symptoms, Causes & Risk Factors.” “Diagnosing and Treating Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA).”
Dodick, D. Headache , March 2003.
American Academy of Sleep Sciences: “Circadian Rhythm Sleep Disorders.”
Colten, H. Sleep Disorders and Sleep Deprivation: An Unmet Public Health Problem , 2006.
American Migraine Foundation: “Medication Overuse Headache.” “Dental Appliances and Headache.”
National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research: “TMJ Disorders.”
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center: “When Is a Headache a Symptom of a Brain Tumor?”
American Brain Tumor Association: “Signs & Symptoms.”
National Institute on Alcohol Abuse: “Drinking Levels Defined.”
Johns Hopkins Medicine: “Headache: Could It Be a Brain Tumor?”
Headache Behind Left Eye: 13 Causes with Treatments
A headache behind the left eye is not a rare condition. The pain can interfere with your work, home duties, and other daily activities. It can be located in the eye, behind the eye, or in the head. This miserable pain may range from mild or dull to a throbbing and sharp stabbing. You may also experience nausea, flashing lights, or sensitivity to light. This pain will make it hard for you to concentrate or fall asleep.
The common causes of a headache behind the left eye are a cluster headache, tension headache, eyestrain, and migraine. However, there are also other causes of why this condition occurs. Knowing the exact cause of a headache can help you deal with it properly.
Headache Behind Left Eye: 13 Common Causes with Treatments
Here are the possible causes of a headache behind the left eye.
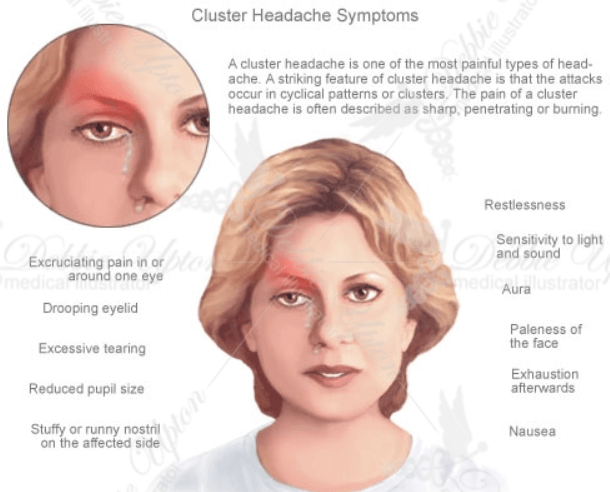
1. Cluster Headache
Cluster headaches, one of the painful types of headache, can occur in clusters or cyclical patterns.
Doctors from the Mayo Clinic say that Cluster headaches usually occur in the middle of the night. The pain can wake you up during your sleep, accompanied by an intense pain around or in one eye.[1]
The periods of pain may last from a few weeks to months, and sometimes even years. This headache is not life-threatening, and treatments can make the pain less severe. The common signs and symptoms of a cluster headache include:
- Intense pain in or around one eye
- Pain radiating to face, neck, and shoulders
- Restlessness and facial sweating
- Redness in one eye
- The runny or stuffy nose on the affected side
- Drooping eyelid and swelling around the eye
Cluster headaches Treatment
An attack may last from fifteen to three hours and may occur every day. With an accurate diagnosis from a professional, you can have proper treatments. Here are some treatments that help you alleviate the symptoms.
- Oxygen inhaling treatment
- Nasal drops – anesthetics
- Physical and breathing exercises
- Drink ginger tea
- Use peppermint essential oil in a diffuser
Preventing cluster headaches
Long-term treatment may result in the prevention or decrease of future cycles. However, it often takes some time to get a hold of the condition. Here are some tips that will help you out:
- Avoid tobacco and alcohol
- Avoid great altitude changes
- Reduce evening and afternoon naps – establish proper sleeping routines
- Limit your exposure to chemical agents
2. Tension Headache
Tension headaches are one of the most common reasons that cause pain behind the eyes.
Doctors from the Healthline say that the pain from a tension headache usually occurs in the neck, forehead, and behind the eyes. It can be mild, moderate, or intense. It feels like a tight strap on your forehead.[2]
This type of headache has many different causes, such as stress, eye dry and eye strain.
Home remedies for tension headaches
- You can take frequent breaks when watching a computer or mobile.
- Using eye drops can also help you get rid of a tension headache effectively.
3. Eyestrain
One of the common causes of a headache behind the left eye is eyestrain. This may occur when the eyes are tired from long and intense use, such as staring at the computer for long hours or driving long distances.
According to Dr. Andrew A. Dahl from Medicinenet, eyestrain usually disappears once you close and rest your eyes. But in rare cases, it can be a sign of an eye problem that requires immediate treatment.[3]
Other signs and symptoms of eyestrain include:
- A headache
- Tired, sore, and itchy eye or eyes
- Blurred vision
- Pain in neck, back, and shoulders
- Increased sensitivity to brightness
Home remedies for eyestrain
- Moisturize your eyes with eye oil such as honey or castor oil.
- Place a cucumber slice over each closed eye to provide them with soothing effects.
- Dab 2 cotton balls in cold milk and place them over the eyes for 5 – 10 minutes.
Tips for prevention
Preventing eye strain is easier than you may think but at the same time harder because you have to adjust your lifestyle.
- Take regular eye breaks, especially if you’re looking at the screen a lot
- Make sure your screen is clean and set to low lighting
- Moisturize your eyes, especially if the air is dry
- Make it a habit of blinking frequently
- Adjust the distance of the monitor
Note: If resting your eyes does not help, see a doctor right away.
4. Migraine
Another possible cause of a headache behind your left eye is a migraine.
A person may experience severe throbbing pain on one side of the head. It is also often accompanied by nausea, sensitivity to sound and light, and vomiting. A Migraine can be disabling when it is severe.
During an attack, you may also experience:
- Lightheadedness, followed by painting
- Throbbing or pulsing pain
- Blurred vision
Natural ways to treat migraine at home
- Mix one tablespoon of honey with one tablespoon of apple cider vinegar in a glass of warm water and drink the solution.
- Apply an ice pack on the head. Make sure that the ice doesn’t come in direct touch with the skin.
- Drink peppermint tea with honey.
Migraine prevention
- Drink a lot of water to stay well-hydrated
- Stick to a gluten-free diet
- Exercise daily
- Sleep for at least 8 hours per day
- Limit stress
Note: If you are experiencing migraines many times already, talk to your doctor about your experiences. If a headache is accompanied by fever, seizures, numbness, double vision, mental confusion, and severe pain, seek medical help right away.
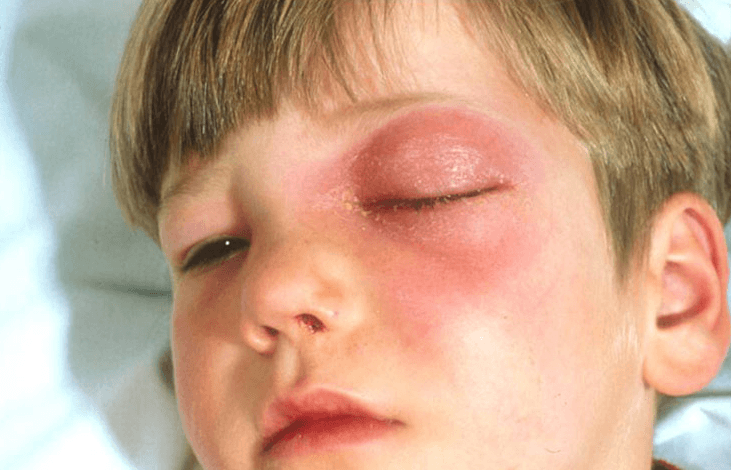
5. Orbital Cellulitis
Orbital cellulitis occurs when the muscles and fat around the eyes become infected. This condition also affects the eyebrows, eyelids, and cheeks. Caused by Haemophilus influenza, Streptococcus pneumonia, or Staphylococcus aureus, orbital cellulitis is a dangerous infection.
Children who are suffering from this condition may lose their vision if the problem gets worse. Other signs and symptoms may include:
- Bulging eyes
- Pain in the upper and lower eyelid
- Pain on cheeks, eyebrows, and when moving the eye
- Blurred vision
- Red or purple eyelid
- Fever
Treating orbital cellulitis at home
- Use a cotton ball to apply tea tree oil to the affected area.
- Apply coconut oil to reduce swelling and redness.
- Mix turmeric, a natural anti-inflammatory agent, with a few drops of tea tree oil to create a paste. Apply this mixture to the swelling.
How to prevent orbital cellulitis
- Balanced diet
- Moderate exercise
- Vaccination
6. Glaucoma
Glaucoma can damage the optic nerve, which happens when the pressure becomes too high.
According to National Eye Institut, people with glaucoma may suffer from severe pain, nausea, blurred vision, and redness of the eye. This condition may also lead to blindness.[5]
While glaucoma is common in older adults, it can occur at any age. Vision loss caused by glaucoma cannot be recovered, so eye checkups to measure the pressure on the eyes is important.
Early diagnosis can slow down or prevent vision loss. The symptoms of glaucoma develop gradually, and they may include:
- Eye redness
- A Severe headache and eye pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Halos around the lights
- Blurred vision
- Patchy blind spots in the side or center vision
- Tunnel vision (advanced stages)
Treatment
Glaucoma can be treated professionally with the use of eye drops and pills. Sometimes, laser surgery is required. You can also try to treat glaucoma at home by adjusting your eating habits. Include the following foods in your diet:
- Carotenoid-rich foods such as oranges and yellow bell peppers
- Wild-caught fish
- Brewer’s yeast
- Fennel plant
- Cherries and blueberries
- Fresh vegetables and fruits
Preventing glaucoma
- Get regular eye checkups
- Exercise your eyes
- Wear eye protection while working
- Take prescribed eye drops
- Limit your caffeine intake
Note: See an ophthalmologist if you develop some of the symptoms, such as blurred vision, eye pain, and headache.
7. A Sinusitis
One of the common causes of a headache behind the left eye is sinusitis. This problem is caused by an infection or allergic reaction in the paranasal sinuses. When the linings of the sinuses become inflamed, congested, or swollen, it can lead to pain.
Dr. Stephanie Watson on Healthline says a sinus infection can cause pain behind your nose, ear, eyes, and cheeks.[4]
Other signs and symptoms of sinusitis may include:
- Thick discharge from the nose
- Postnasal discharge or drainage down the back of the throat
- Nasal congestion
- Stuffy nose
- Reduced sense of smell and taste
- A cough
Home remedies for sinusitis
- Drink lots of fluids
- Prepare steam with menthol or eucalyptus oil and hold your head above to breathe it in.
- Use saline water to flush your nasal passages
- Eat spicy foods
- Humidify the air
- Apply warm compress
Sinusitis prevention tips
- Regularly flush your nasal passages with saline solutions
- Drink sufficient amounts of water
- Boil water and inhale the steam or take hot showers
- Avoid smoking
- Humidify the air in your home
Note: If your symptoms do not improve, see a doctor right away.
8. Vision Issues – Optic Neuritis
This condition occurs when the optic nerve is inflamed, caused by the loss or damage of the sheath that protects it. Optic neuritis is common in people who have multiple sclerosis.
Other causes of this condition include ocular herpes, sinusitis, nutritional deficiency, toxins such as tobacco and alcohol, infections like toxoplasmosis, and heredity. Other symptoms that one may experience are:
- Pain in the eye
- Loss of vision in one eye
- Side vision loss
- Loss of color perception
- Flickering lights when moving the eyes
Treatment
Most cases of optic neuritis resolve on their own. The vision may return within two weeks to 12 months. Treatment may vary depending on the underlying cause.
- Steroid treatment is usually recommended. It is also used for slowing down or lowering the risk of developing multiple sclerosis.
- Plasma exchange therapy might help if steroid therapy fails to recover vision.
- Include soybean milk, barley brew, apple, spinach, and other healthy foods to accelerate the healing process.
Prevention
- Minimizing your risk of acquiring infections (bacterial and viral) lowers the risk of optic neuritis.
Note: This condition can be serious. If you develop, any of these symptoms or the symptoms are getting worse, seek medical help immediately.
9. Pain From Dry Eyes
Dry eyes syndrome is also one of the causes of a headache behind the left eye. It is a condition that happens when the tears are not providing enough lubrication for the eyes. This may feel uncomfortable as it may burn or sting.
You can experience dry eyes when staring at a computer for a long time, riding a bicycle, or staying in an air-conditioned room. This can be treated by changing your lifestyle or using eye drops. Other symptoms that may develop include:
- Burning or scratchy feeling in the eye or eyes
- Light sensitivity
- A feeling of having something in the eyes
- Difficulty driving at night
- Watery eyes (your body’s response to irritation caused by dry eyes)
- Eye fatigue
- Blurred vision
Ways to treat dry eyes
- For most people, over-the-counter eye drops help in adding lubrication.
- Apply a warm towel over your eyes for about five minutes.
- Wash your eyelids frequently with mild soap.
- Use a humidifier to add moisture to the room.
Prevention
- Eat foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as ground flaxseed, fish oils, almonds, chia seeds, and sesame seeds.
- Always massage your tear glands to prevent dry eyes.
10.Scleritis
Scleritis is the inflammation of the white part of the eye (sclera). This serious disease is often related to autoimmune disorders, and prompt treatment is needed to prevent vision loss.
Scleritis is often associated with arthritis, systemic lupus erythematous IQ, mixed connective tissue disease, Sjogren’s syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease, allergic angiitis, progressive systemic sclerosis, and polyarteritis nodosa. Other symptoms of Scleritis may include:
- Blurred vision or double vision
- Excessive tearing
- Sensitivity to light
- Redness of the white portion of the eye
- Pain when moving the eyes
- Eye irritation
- Deep-seated headaches
How to treat Scleritis
- Your doctor may prescribe nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce inflammation and pain.
- If NSAIDs don’t work, corticosteroid pills may be used.
- Foods rich in vitamins A, B12, C, and D
How to prevent Scleritis
This condition cannot be directly prevented. Those who have systematic inflammatory diseases should manage the underlying cause to prevent Scleritis from occurring and aggravating.
Note: Severe scleritis may require surgery. Seek medical help for early treatment.
11. Ocular Migraine
One of the possible causes of a headache behind the left eye is an ocular migraine.
Doctors from WebMD say that an ocular migraine can make you get vision loss in one eye for a short time. This migraine involves visual disturbances, and it may develop with or without pain. During an attack, you may see flashing or zigzagging lines.[6]
While an ocular migraine is not a serious condition, it may also cause blind spots and interfere with your daily tasks such as driving, reading, or writing.
Other symptoms of an ocular migraine are:
- Partial vision loss
- Blank spots in vision
- Flashes of light
- Dimming or blurring
Ocular migraines usually last for less than five minutes up to thirty minutes.
Natural techniques for treating ocular migraine
- Drink basil tea and prepare steam with a few drops of basil essential oil in it
- Massage the back of your head and the neck with peppermint or lavender essential oil
- Drink chamomile tea
- Practice yoga to reduce mental clutter
How to prevent an ocular migraine
- Decrease stress
- Avoid smoking
- Avoid birth control pills
- Exercise regularly
- Avoid high altitudes
- Stay well-hydrated
- Avoid excessive heat
12. An aneurysm
A brain aneurysm is a bulging in the wall of an artery in the brain. In most cases, this condition does not develop symptoms. When the aneurysm leaks or ruptures, it results in subarachnoid hemorrhage or bleeding into the brain.
A ruptured aneurysm is dangerous and requires immediate medical attention. An unruptured aneurysm, which causes symptoms and creates health issues, should be treated right away to prevent a rupture. The symptoms of an aneurysm include:
- A severe headache that is different from a regular or a past headache
- Nausea and vomiting
- Neck pain
- Sensitivity to light
- Loss of consciousness
- Seizures
Aneurysm treatment
Depending on the type, the aneurysm is usually treated with medications or through surgery. The two main surgery techniques include open chest or open abdominal repair and endovascular repair. The purpose of the treatment is to prevent an aneurysm from getting worse and damage body structures.
Prevention tips
The best way to prevent an aneurysm is by avoiding the factors that may cause it. Make sure to:
- Quit smoking
- Establish a healthy diet rich in whole grains, vegetables, fruits, and protein-rich foods
- Stay physically active
- The risk of a ruptured aneurysm may increase due to smoking, high blood pressure, and family history.
13.Eye Pain from Brain Infection
Bacteria, fungi, or viruses can cause brain infections. This condition may also involve the spinal cord. Infections cause encephalitis or inflammation of the brain. The most common causes of encephalitis are viruses.
Another brain infection that leads to inflammation of the meninges, layers of tissue covering the spinal cord and the brain, is meningitis. When both the meninges and the brain are infected, this condition is called meningoencephalitis.
Abscessed look like boils that can form on any part of the body, including the brain. Empyema is another infection that forms in a space in the body, such as the space between the lungs or the brain.
The treatment for brain infection depends on the underlying cause.
- Antibiotics may be given and other medications for a headache and fever.
- Those with respiratory problems will receive oxygen.
- Anticonvulsants may be used to treat or prevent seizures.
- Steroids may be given in case of brain swelling.
- In the case of a brain abscess, drainage will be performed by a neurosurgeon.
Seek medical attention if you suspect that someone has a brain infection. Some tips that may be useful include:
- Provide cooling measures to alleviate fever.
- Follow the doctor’s advice and avoid any extreme activities.
These are the most common causes of a headache behind the left eye. When you experience unusual headaches, see a professional right away for early diagnosis and treatment.
Why Your Head Hurts Behind Your Left Eye?
Headaches have the tendency to develop at just about any time anywhere. It can affect you while working, in your home, or when you are doing daily activities. The pain of a headache can be throbbing or dull, sharp or located in a pinpoint area of the head. Headaches are miserable and all you want to do is to let the pain go away. If you can identify the cause of the headache, it can help manage the headache and can prevent getting other headaches in the future. But what about having a headache behind the left eye?
What Causes Headache Behind Left Eye?
A headache behind the left eye is not an uncommon condition. There are many people who have these kinds of headaches for various reasons. The pain may originate in the head or in the eye. While you can have both conditions at the same time, a headache behind eye doesn’t mean you are suffering from simultaneous eye pain and head pain.
In many cases, if the headache is due to eye problems, it would mean that there is some kind of disease of the eye or surrounding tissues, including the muscles that make the eyeball to move, the nerves around the eye, and the eyelid. In some situations, eye pain is unrelated to problems with the eye at all, regardless of the location of the pain.
Possible causes include the following:
1. Migraine Headaches
Migraine headaches are a type of headache with no definable cause. It is thought to be the result of an abnormal flow of blood to the brain. While the exact reason behind getting a migraine headache is unclear, there are identifiable triggers, including a lack of sleep, psychological stress, hormonal changes, and eating certain types of foods. Most will complain of pain behind one or both eyes as well as sensitivity to light.
2. Cluster Headaches
Cluster headaches are considered to be one of the severest types of headaches, but they are less common than migraine headaches. Those who suffer from them describe a stabbing, throbbing or intense burning type of pain that occurs frequently throughout the day for several days or weeks, but then it goes into remission and doesn’t occur for many months or years later. Most people complain of headache behind left eye or right eye and it usually does not travel to the other eye.
3. Eyestrain
Eyestrain is a very common cause of pain located behind the eyes. It is more common now because people spend a lot of time using computers and watching television. It can be due to not blinking enough as well as straining of the muscles that move the eyeballs. Eyestrain is more prevalent in people who have refractive disorders of the eye, such as those with astigmatism, nearsightedness or farsightedness and who don’t wear their eye glasses as directed. Other symptoms include excessive tearing, dryness of the eye and eye redness along with blurry vision, tired eyes, and pain in the eye. Eyestrain is also associated with tension headaches.
4. Sinusitis
Sinusitis is a common cause of headache behind left eye. The problem is due to an allergic reaction or infection in the paranasal sinuses. The tissue that lines the sinuses becomes swollen, congested, and inflamed, leading to the pain. Exactly where the pain is located depends on which of the various sinuses are involved. For example, maxillary sinusitis leads to pain in the cheek, whereas sinusitis in the fontal sinuses leads to pain right above the eyes. And sinusitis in the sphenoid sinuses leads to pain located behind the eyes.
5. Orbital Cellulitis
This is an infection of the eye that is usually related to the eyelids. It is more common in children as a complication of having a sinus infection. This can be a dangerous infection that can result in blindness if not treated promptly. Besides the eye pain, there is visible swelling of the eye tissues, including the cheeks, eyebrows, and eyelids. The eyes may actually be bulging and moving the eyes is difficult with extreme pain.
6. Optic Neuropathy
This is a medical condition in which there is disease or damage to the optic nerve in the eye. It is a dangerous eye condition that can lead to total blindness in the affected eye. The various causes of optic neuropathy include toxic exposures, nutritional problems, infections, neurological diseases, and certain hereditary conditions. It can also be a complication of having a sinus infection. There are obvious disturbances in vision along with eye pain that worsens when the sufferer moves the eyes.
7. Head Injury
A head injury can cause secondary complications of a fractured skull or increased pressure within the brain from swelling or bleeding. A typical symptom of head injury is a headache behind left eye, right eye, or both eyes. Head injuries are commonly associated with sports related injuries, motor vehicle accidents, assaults, and falls from a great height. If a person is suffering from a traumatic head injury, this should be thoroughly evaluated to make sure there are no secondary complications.
8. Glaucoma
This is a condition that happens when the pressure within the eye itself becomes too high, causing damage to the affected eye. Common symptoms include pain behind the eye and damage to peripheral vision. Eventually, the optic nerve can be damaged and blindness can ensue. This condition occurs at a higher rate among African Americans aged 40 and above.
9. Aneurysm
An aneurysm in the brain can be a cause of headache behind left eye. This occurs when there are damaged blood vessels within the brain that burst completely or leak blood, causing a hemorrhagic stroke. Other causes of hemorrhagic stroke and headache include having a subarachnoid hemorrhage, which is bleeding between the brain tissue and the arachnoid lining of the brain. The headache is usually very severe and can be located anywhere on the head.
10. Tumor or Brain Infection
While these conditions are very rare, they can be the cause of pain behind left eye. The brain tissue itself is generally not the source of the pain, instead, the pain is caused by cancer, a brain abscess, infection or encephalitis, which can damage blood vessels and associated nerves near the eye, leading to the eye pain.
This is not the full list of causes of headache behind left eye. Whenever you or someone near you experiences such kind of condition, see a doctor for early diagnosis and treatment.
Below is a video that helps to relieve the eye strain that almost everyone may experience, please follow the instructions to reduce the stress on them.